Provides Jenkins integration for NodeJS & npm packages.
To install Jenkins on Ubuntu, use the command: sudo apt update. Sudo apt install Jenkins. The system prompts you to confirm the download and installation. Press Y and hit Enter, and the system downloads and installs Jenkins. To check Jenkins was installed and is running enter: sudo systemctl status jenkins. Homebrew Installer Jenkins can be installed using the Homebrew package manager. Homebrew formula: jenkins-lts This is a package supported by a third party which may be not as frequently updated as packages supported by the Jenkins project directly. Sample commands: Install the latest LTS version: brew install jenkins-lts Install a specific LTS version: brew install jenkins.
Download & Installation
You can download the latest .hpi and install it from the Manage Plugins menu, or install this plugin directly from the Plugins Update Center.
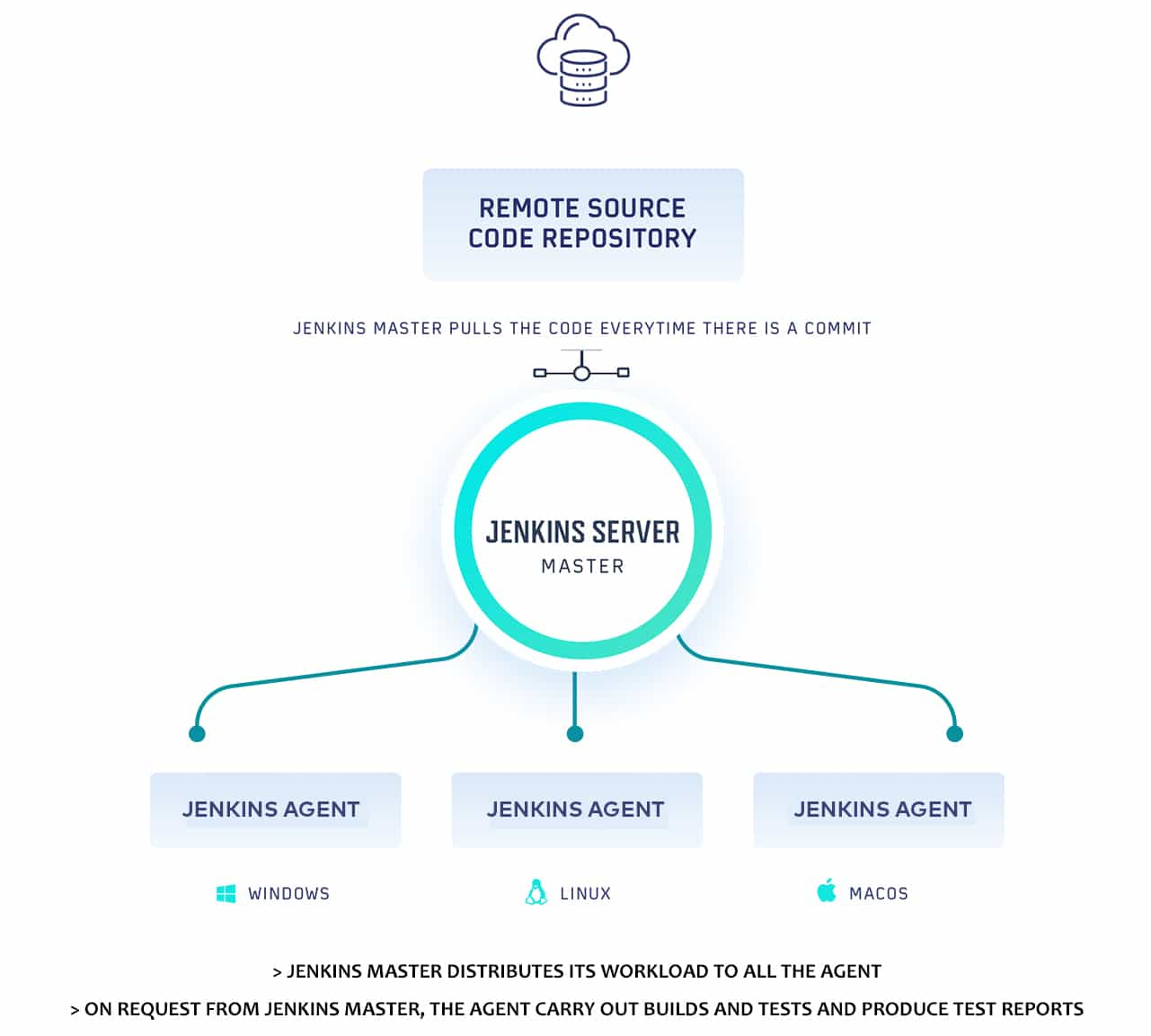
Jenkins Tutorial
Main features
- Provides NodeJS auto-installer, allowing to create as many NodeJS installations 'profiles' as you want.
The auto-installer will automatically install a given version of NodeJS, on every jenkins agent where it will be needed - Allows to install globally some npm packages inside each installations, these npm packages will be made available to the PATH
- Allows to execute some NodeJS script, under a given NodeJS installation
- Allows use custom NPM user configuration file defined with config-file-provider plugin to setup custom NPM settings
- Add a lightweight support to DSL pipeline
- Force 32bit architecture
- Relocate npm cache folder using pre defined strategies
- Allow use of a mirror repo for downloading and installing NodeJS.
Usage
After installing the plugin, go to the global jenkins configuration panel (JENKINS_URL/configure or JENKINS_URL/configureTools if using jenkins 2),
and add new NodeJS installations.- If you wish to install NodeJS from a nodejs.org mirror, select the 'Install from nodejs.org mirror' option, where you can then enter a mirror URL and then install NodeJS just like you would from nodejs.org.
For every Nodejs installation, you can choose to install some global npm packages.
Since 1.2.6 you could force the installation of the 32bit package for the underlying architecture if supported. If the package is not available the build will fail.Note that you might provide npm package's version (with syntax 'package@0.1.2' for instance, or maybe better, 'package@~0.1.0') in order to enforce
reproductibility of your npm execution environment (the ~ syntax allows to benefits from bugfixes without taking the risk of a major version upgrade)
See below:Now, go to a job configuration screen, you will have 2 new items :
- On the 'Build environment' section, you will be able to pick one of the NodeJS installations to provide its bin/ folder to the PATH.
This way, during shell build scripts, you will have some npm executables available to the command line (like bower or grunt)
See below: - On the 'Build' section, you will be able to add a 'Execute NodeJS script' build step
This way, you will be able to fill a textarea with the script content you want to execute.
Note that you will have to select a NodeJS runtime you previously installed, to specify the NodeJS version you want to use
during your NodeJS script execution.
- On the 'Build environment' section, you will be able to pick one of the NodeJS installations to provide its bin/ folder to the PATH.
You can customise any NPM settings you need creating a NPM config file where you can also setup multiple npm registry (scoped or public)
and select for each one stored credential (only user/password supported type) as follow:
and than select the config file to use for each configured build stepYou would relocate the npm cache folder to swipe out it when a job is removed or workspace folder is deleted. There are three default strategy:
- per node, that is the default NPM behaviour. All download package are placed in the ~/.npm on Unix system or %APP_DATA%npm-cache on Windows system;
- per executor, where each executor has an own NPM cache folder placed in ~/npm-cache/$executorNumber;
- per job, placed in the workspace folder under $WORKSPACE/npm-cache. This cache will be swipe out together the workspace and will be removed when the job is deleted.
Pipeline
Jenkins Download For Mac
The current supported DSL steps are:
- nodejs (as buildwrapper)
- tools
In a Declarative pipeline you can add any configured NodeJS tool to your job, and it will enhance
the PATH variable with the selected NodeJS installation folder, instead in scripted pipeline you have to do it manually.
Example of use tools in Jenkinsfile (Scripted Pipeline)
This example show the use of buildwrapper, where enhanced PATH will be available only inside the brace block

Example of the use of buildwrapper Jenkinsfile (Declarative Pipeline)
Configure plugin via Groovy script
Either automatically upon Jenkins post-initialization or through Jenkins script console, example:
Known limitations / issues
NodeJS version 1.0 has adapted its code to the most recent Jenkins API (1.6xx). If also EnvInject is installed you will fall in JENKINS-26583
that corrupts setup of the nodejs installation bin folder into PATH environment. In this case consider if update or not or use an own build from
this branch until the JENKINS-26583 will not be fixed.
- If you update from NodeJS 0.2.2 or earlier to newer version materializes a data migration. This data migration is transparent to the users but
you can not back to 0.2.2 without lost global configuration tools and job build step configuration. - NodeJS versions prior to 0.9.0 won't be available at the moment (directory structure was not the same as today on distribution site).
This might be handled in the future (this is exposed as PathResolver implementation) :
don't hesitate to provide new implementations for previous versions and submit a PR on github. - Supported architecture are:
- Windows 32/64 bit
- Linux 32/64 bit
- OSX (intel) 64 bit
- Arm 6l/7l/64
- SunOS
- AIX
Releases Notes
Please refer to github repository page
Comments are closed.